Non Echo Planar Dwi

Figure 1 From Diffusion Weighted Imaging Dwi In Mr Mammography Mrm Clinical Comparison Of Echo Planar Imaging Epi And Half Fourier Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo Haste Diffusion Techniques Semantic Scholar
Echo Planar Imaging Epi Questions And Answers In Mri
Http Pdf Posterng Netkey At Download Index Php Module Get Pdf By Id Poster Id

Diffusion Weighted Imaging With Dual Echo Echo Planar Imaging For Better Sensitivity To Acute Stroke
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro
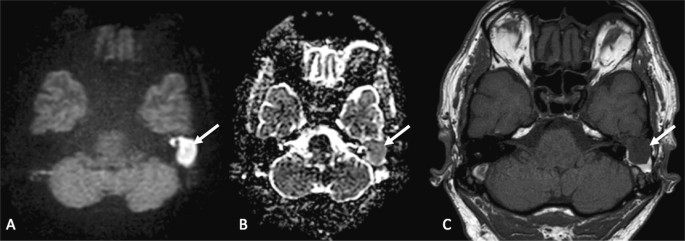
Importance Of Signal Intensity On T1 Weighted Spin Echo Sequence For The Diagnosis Of Chronic Cholesteatomatous Otitis Springerlink
( 13 ) Evaluating the utility of non echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the preoperative evaluation of cholesteatoma:.
Non echo planar dwi. This can also be used to diagnose residual or recurrent cholesteatoma in patients who have undergone intact canal wall mastoidectomy. Non‐echo‐planar imaging (EPI) MRI has been recently introduced to improve the detection of small‐sized cholesteatoma and decrease different artefacts occurring in the EPI‐diffusion‐weighted (DW) technique. In the comparison of preoperative evaluation for cholesteatoma and intraoperative findings.
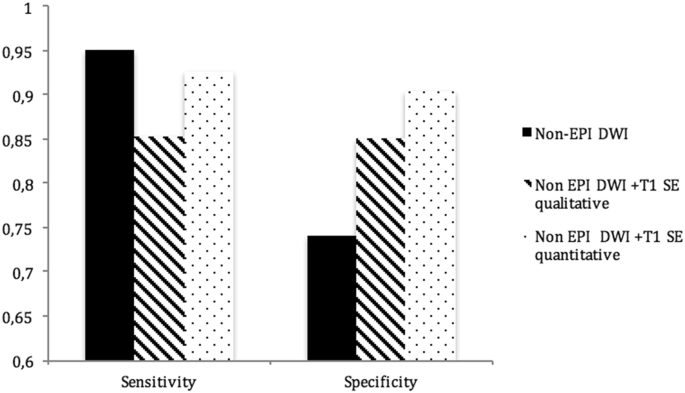
In CWD cases, as there is an open mastoid cavity that can be directly examined through otomicroscopy, residual or recurrent disease can often be detected and managed with microsuction in the clinic. To qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate image quality and compare the diagnostic value of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) based on turbo spin-echo (TSE) and echo-planar imaging (EPI), to distinguish rNPC from post-chemoradiation fibrosis. New non–echo-planar DWI sequences, such as periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction, are superior to conventional echo-planar DWI, since they minimize susceptibility artifacts at the skull base and increase sensitivity for detection of lesions as small as 2 mm.
On the DWI images with b-value 1000 s/mm 2, a cholesteatoma becomes apparent as a hyperintense area. To investigate the feasibility of using diffusion-weighted (DW) echo-planar imaging (EPI) for differentiating primary parotid gland tumors. To assess the utility of DWI with echo-planar (EPI-DWI) and non-echo-planar (PROPELLER) sequences for the diagnosis of primary and recurrent cholesteatoma.
A large prospective multicentre randomized controlled study could validate the findings and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of DWI as an alternative for second-look surgery (control arm) in managing cases of. Peter Mansfield received the Nobel Prize in 03 for his contribution in the development of MRI and EPI in particular. The standard examination is a T2-weighted series in the coronal and axial plane, followed by a non-echo planar DWI series (b-values 0, 1000).
To examine the novel use of non-echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) in depicting activity and treatment response in active Grave’s orbitopathy (GO) by assessing, with inter-observer agreement, for a correlation between its apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) and conventional Short tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) MRI signal-intensity ratios (SIRs). Non-echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (NEDWI) combined with T2 weighted imaging acquisition using HASTE (half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo) has been shown to be more accurate in diagnosing cholesteatoma within the post-operative ear than the standard echo-planar diffusion weighted imaging (EPDWI) routinely used to identify acute stroke (7). This has the advantage of speed but suffers from susceptibility artifacts/distortions, low signal-to-noise, and spatial blurring.
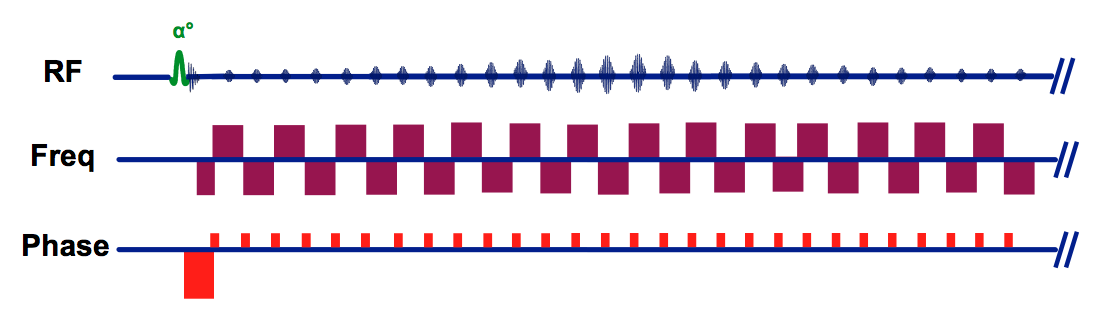
Non-EPI DWI is a promising alternative to second-look surgery for the. Between the specificity measurements. As originally defined, echo planar imaging referred to a sequence in which data from all of k-space for an entire 2D plane was collected following a single RF-excitation pulse.
A spin-echo sequence is typically used, specifically echo-planar imaging (EPI). We prospectively assessed the diagnostic accuracy of MRI including delayed post. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) provides surgeons with a superior imaging tool to more accurately diagnosis cholesteatoma which are to be treated using transcanal endoscopic ear surgery (TEES).
439 - 444. Since 06, non echo planar imaging (EPI) Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (sequences has shown high accuracy to depict recurrent cholesteatoma. Dremmen MH, Hofman PA, Hof JR, Stokroos RJ, Postma AA (12) The diagnostic accuracy of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the detection of residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma of the temporal bone.
To date non-EPI is. In this way, central k-space is. The non-echo planar diffusion-weighted MRI (non-EP DWI) sequence is efficient in identifying the restricted diffusion in the substance of cholesteatoma, and, thanks to its sensitivity and precision, has changed the way otolaryngologists manage chronic ear disease.
The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of HASTE DWI for the detection of incipient cholesteatoma in high-risk retraction pockets. The diagnostic accuracy of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the detection of residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma of the temporal bone. The purposes of this study were to determine the feasibility of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with a single-shot echo-planar sequence and parallel technique for depicting endometrial cancer and to examine the role of this technique in preoperative assessment.
Non-echo planar diffusion weighted MRI (NEDWI MRI) is accurate in detecting cholesteatoma in the post-operative ear but the effect on surgical decision-making in the setting of revision mastoid surgery using surgical histopathology as the gold standard has not been investigated. Two different DWI techniques are currently in use :. Mas-Estelles F, Mateos-Fernandez M, Carrascosa-Bisquert B, et al.
21, 22 Previous studies have also demonstrated this finding using echo-planar-DWI, but to our knowledge, this is the first demonstrating a positive relationship, using non-EPI-DWI. Several studies have shown that the echo planar imaging (EPI) DWI sequence and post gadolinium MRI are less accurate than non-echo planar diffusion weighted MRI (non-EPI DWI), possibly due to the higher susceptibility of EPI for magnetic interface artifacts and the lower image quality of post gadolinium , , , , , , ,. In the modern lexicon these are termed single shot.
More recently the term has been expanded to include any rapid gradient-echo or spin-echo sequence in which k-space is traversed in one or a small number of excitations. To examine the novel use of non-echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) in depicting activity and treatment response in active Grave's orbitopathy (GO) by assessing, with inter-observer agreement, for a correlation between its apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) and conventional Short tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) MRI signal-intensity ratios (SIRs). However, many authors have favoured non‐echo‐planar DWI as it is less susceptible to the skull base distortion that can occur because of the presence of an air–bone interface.
Postma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:. RS-EPI, readout-segmented echo planar imaging. This technique is also time saving in comparison to delayed post‐contrast imaging.
Non-echo-planar DW MRI is highly sensitive and specific in identifying middle ear cholesteatoma. Two diffusion gradients are added either side of the 180º RF pulse. Non–echo-planar imaging (non-EPI) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is an accurate noninvasive imaging option that can be used in diagnosing primary cholesteatoma.
1247 - 1250 6. High sensitivity and negative predictive value and relatively lower specificity and positive predictive value are achieved by a single non-echo planar DWI protocol. Non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging represents an alternative to resolve this problem, once this method is less subject to this type of artifact, besides offering images with higher spatial resolution and thinner slice thickness, allowing the detection.
Compared with the EP DWI sequence, the non-echo-planar diffusion weighted imaging (non-EPI) DW imaging sequence produces thinner slices and has a higher imaging matrix, and it tends to produce fewer magnetic susceptibility artifacts but requires longer imaging times (multi-shot non-echo-planar DWI sequences require approximately 8 min), and non-EPI has higher sensitivity for detecting cholesteatoma and a lower misdiagnosis rate 7, 10, 11, 12. Both echo‐planar and non‐echo‐planar DWI techniques have been utilised in detecting cholesteatoma. This study investigated the use of echo planar imaging (EPI) and half-Fourier.
This is important as DWI images the very small motion of water molecules which will be masked by any macroscopic body motion. Li PM , Linos E , Gurgel RK et al. EPI minimises the effect of patient motion as it is a very quick sequence.
Even in diagnostic testing with high sensitivity and specificity, false positives and false negatives occur. Non-echo-planar DWI MR imaging (including the HASTE sequence) has been shown to be highly sensitive and specific for large cholesteatomas. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) techniques have shown potential to differentiate between benign and malignant neoplasms.
Non-EPI DWI is a promising alternative to second-look surgery for the detection of residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma. To evaluate non echo-planar diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (non-EP DW MRI). Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) is an alternative to second-look surgery for the detection of cholesteatoma.
None of the non-operated RS-EPI positive mismatched lesions and only one of the non-operated mismatched non-EPI positive cases was clinically suspected to have cholesteatoma over 469 ± 162 days of follow-up. Non-echo planar (non-EPI) and echo planar (EPI) DWI. The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of HASTE DWI for the detection of incipient cholesteatoma in high-risk retraction pockets.
If EPI sequences had a high rate of diffeomorphic atefacts whereas non EPI sequences using either HAlf-Fourier acquisition Single-shot Turbo spin-Echo (HASTE) or Fast. Fifty consecutive patients with a suspected primary tumor of the parotid gland were examined with a DW EPI sequence (TR 1,500 msec, TE 77 msec, field of view 250 x 250 mm, pixel size 2.10 x 1.95 mm, section thickness 5 mm). AIM:To examine the novel use of non-echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) in depicting activity and treatment response in active Grave's orbitopathy (GO) by assessing, with inter-observer agreement, for a correlation between its apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) and conventional Short tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) MRI signal-intensity ratios (SIRs).
Non-echo-planar DWI MR imaging (including the HASTE sequence) has been shown to be highly sensitive and specific for large cholesteatomas. Two different DWI techniques are currently in use:. Non-echo-planar DWI is highly sensitive and specific in detecting cholesteatoma.
1197 - 1213 5. Were scheduled for second-look-surgery after primary canal wall up repair of cholesteatoma underwent 1.5 T MRI including non-EP DWI and high-resolution coronal T1 and T2-FS SE sequences. Non-echo planar DWI for cholesteatoma diagnosis can be performed on 1.5T or 3T scanners indifferently.
Non-echo planar (non-EPI) and echo planar (EPI) DWI. On the ADC map, a low signal should be visible in the same area, confirming the presence of diffusion restriction. Abstract BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:.
DW MRI may help to stratify patients into groups of who would benefit from early second-look surgery and those who could be closely observed. Echo-planar imaging (EPI), was invented by Sir Peter Mansfield in 1977 (Mansfield, 1977) long time before major companies invested in the development of clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which started in honest in 19. The signal intensity should be higher than visible on the DWI images with b-value 0 s/mm 2.
A prospective study of 33 ears, 21 with previous cholesteatoma surgery. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Conventional diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is typically performed using a single-shot echo-planar (ss-EPI) sequence.
Developed by renowned radiologists in each specialty, STATdx provides comprehensive decision support you can rely on - Pars Flaccida Cholesteatoma. However, the diagnostic significance of using DWI under routine conditions remains unclear. All patients underwent non‐echo planar HASTE diffusion‐weighted imaging prior to being offered ‘second‐look’ surgery.
Contemporary non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging of middle ear cholesteatomas. Non-echo planar DWI is currently the imaging modality of choice due to its high diagnostic performance in the detection of post-operative cholesteatoma 1-3. We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy, expressed as a positive predictive value, of MR imaging for the detection of residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma in our hospital.
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Echo-Planar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Detection of Residual and/or Recurrent Cholesteatoma of the Temporal Bone M.H.G. Radiological findings were correlated with second‐look intra‐operative findings in 38 cases with regard to presence, location and maximum dimensions of cholesteatoma.

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics
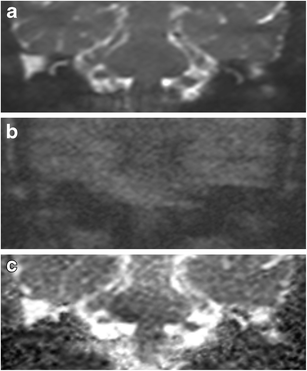
Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Post Operative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Navigating Beyond The Pitfalls To Find The Pearl Insights Into Imaging Full Text

Pdf Role Of Diffusion Weighted Mr In Differential Diagnosis Of Intracranial Cystic Lesions Yasar Bukte Yahya Paksoy And Emine Genc Academia Edu

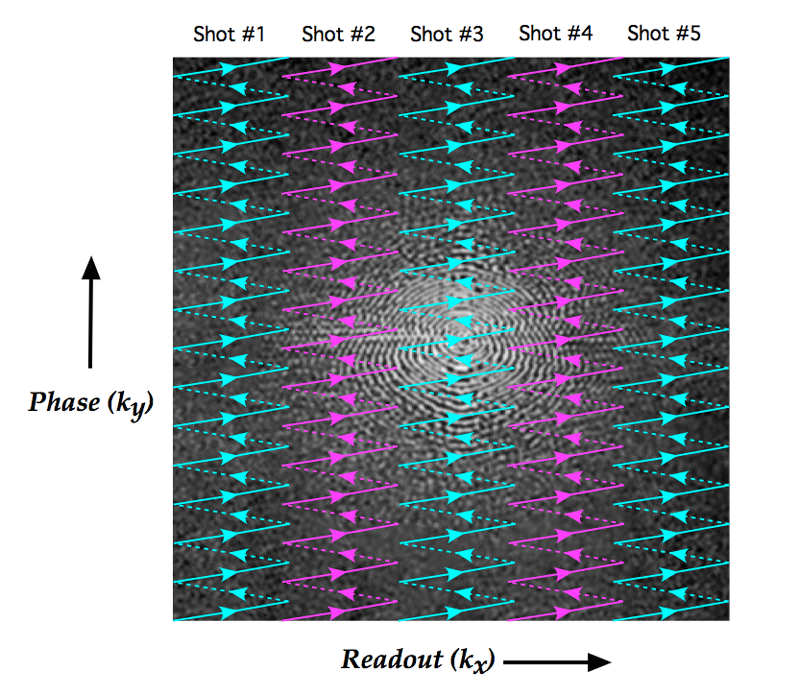
Multi Shot Cartesian Tse Dwi With Inherent 2d Phase Correction Zhe Zhang1 Xiaodong Ma1 Bing Zhang2 Ming Li2 Chun Yuan1 3 And Hua Guo1 1center For Biomedical Imaging Research Department Of Biomedical Engineering School Of Medicine

Accuracy Of Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging Signal Intensity Measurements For The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Abstract Europe Pmc
2

Comparison Of Multiplexed Sensitivity Encoding And Single Shot Echo Planar Imaging For Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of The Liver European Journal Of Radiology
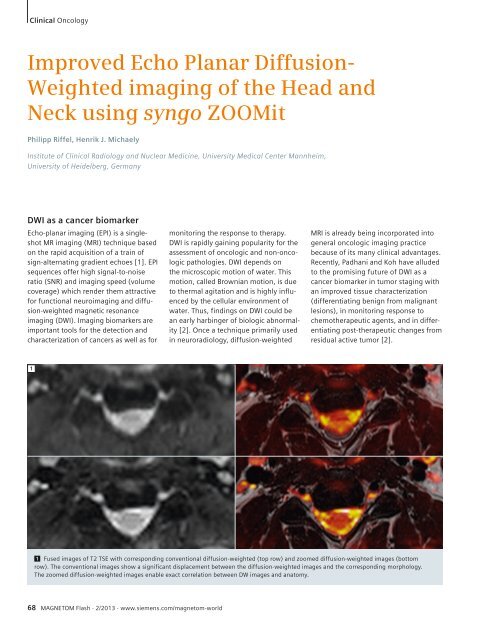
Improved Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of The Head And
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Rg

Non Epi Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Siemens Healthineers Belgium

A A 60 Year Old Male Suspected Of Having A Primary Acquired Middle Ear Download Scientific Diagram

Turbo Spin Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri For Cholesteatoma In Revision Mastoidectomy A Prospective Study Of Diagnostic Accuracy And Clinical Impact Paddle Australian Journal Of Otolaryngology

Resolve Multishot Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Clinical Mri
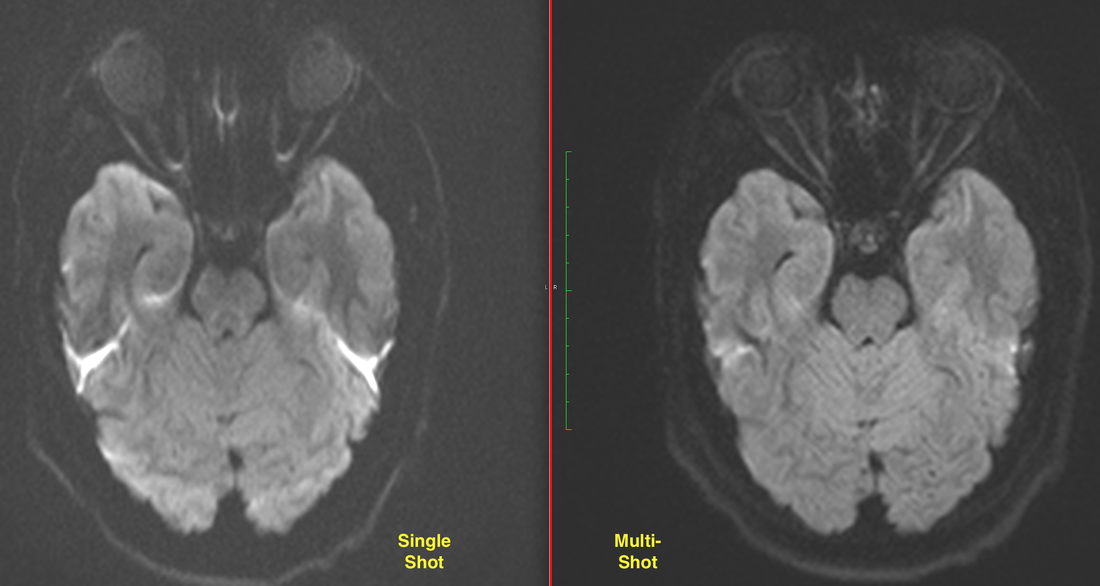
Comparison Of Different Dwi Techniques A Epi Dwi Acquired In A Download Scientific Diagram

Optimization Of Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging With Parallel Imaging In Healthy Pancreas Yu Nishina1 Satoru Morita1 Tatsuya Kuramoto2 Makoto Suzuki2 Hitoshi Tadenuma2 Yasuhiro Goto2 Masami Yoneyama3 And Shuji
Magnetism Questions And Answers In Mri

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics
Intensity Corrected Dual Echo Echo Planar Imaging De Epi For Improved Pediatric Brain Diffusion Imaging
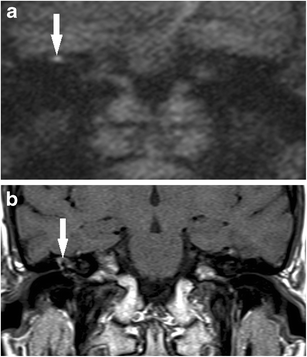
Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Post Operative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Navigating Beyond The Pitfalls To Find The Pearl Insights Into Imaging Full Text

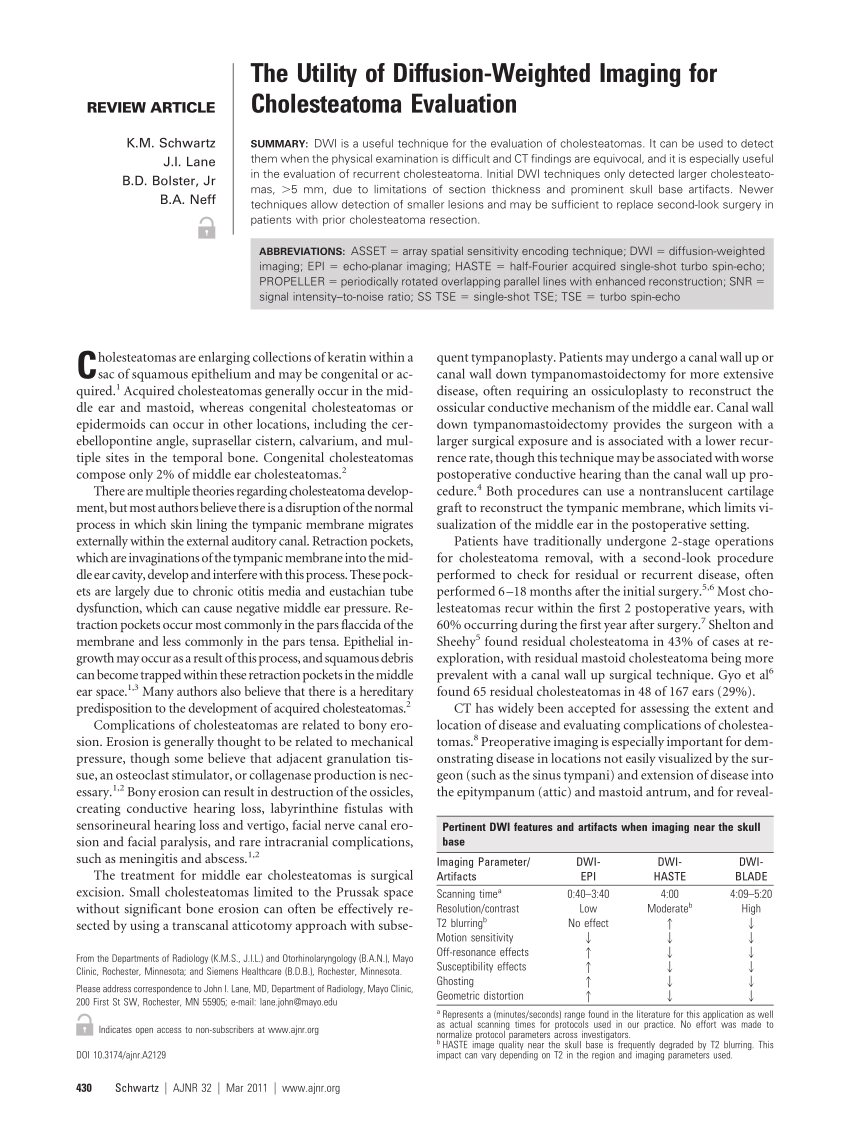
The Utility Of Diffusion Weighted Imaging For Cholesteatoma Evaluation American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Ge Signapulse Autumn 18 Diffusion Imaging Demystified

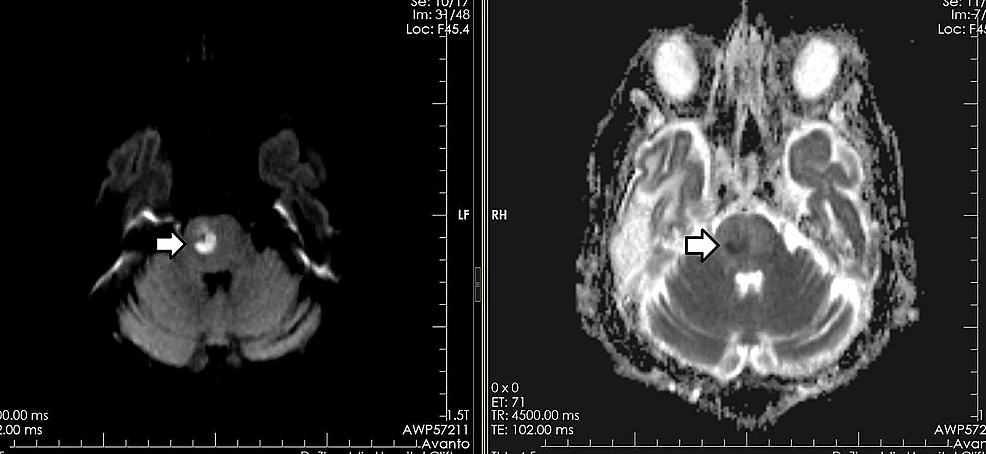
Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding
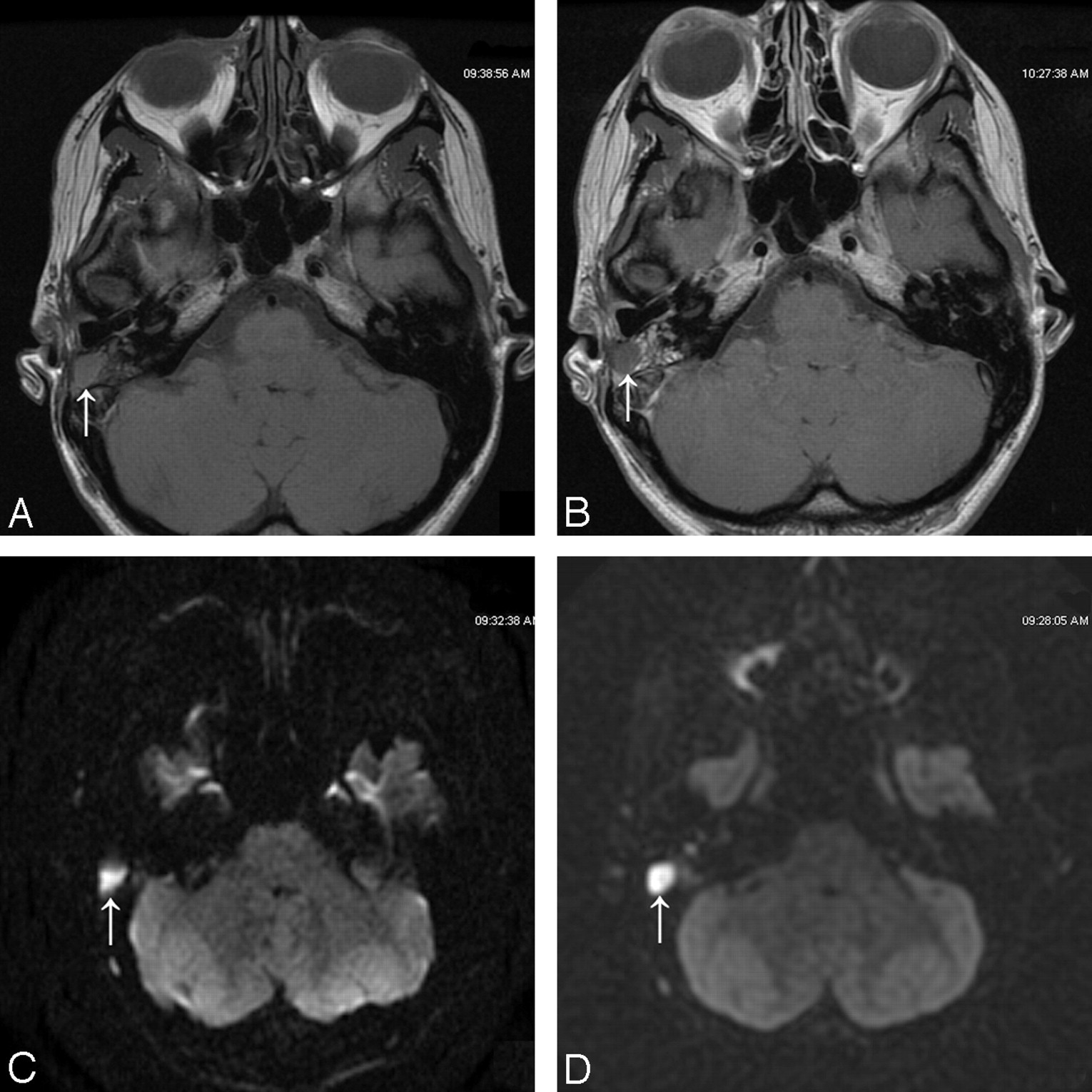
3t Mr Imaging Of Postoperative Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Value Of Periodically Rotated Overlapping Parallel Lines With Enhanced Reconstruction Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging American Journal Of Neuroradiology
2

Gross Tumour Volume Delineation In Anal Cancer On T2 Weighted And Diffusion Weighted Mri Reproducibility Between Radiologists And Radiation Oncologists And Impact Of Reader Experience Level And Dwi Image Quality Radiotherapy And

Diffusion Weighted Mri Of Cholesteatomas Of The Petrous Bone Fitzek 02 Journal Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Wiley Online Library

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr Ztbjwdl Oubftfkbu36dlpadsoctlt7ssdt Fu7hvnsts4jo Usqp Cau

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics
Http Pdf Posterng Netkey At Download Index Php Module Get Pdf By Id Poster Id

Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Of Primary And Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma An Assessment By Readers With Different Expertise

Non Epi Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Siemens Healthineers Belgium

Diffusion Weighted Imaging Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Detectability And Anatomical Correlation Of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Using Fused Thin Slice Non Echo Planar Imaging Diffusion Weighted Image And Magnetic Resonance Cisternography Fts Nepid Semantic Scholar

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding
Readout Segmented Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mr For The Evaluation Of Aggressive Characteristics Of Rectal Cancer Scientific Reports
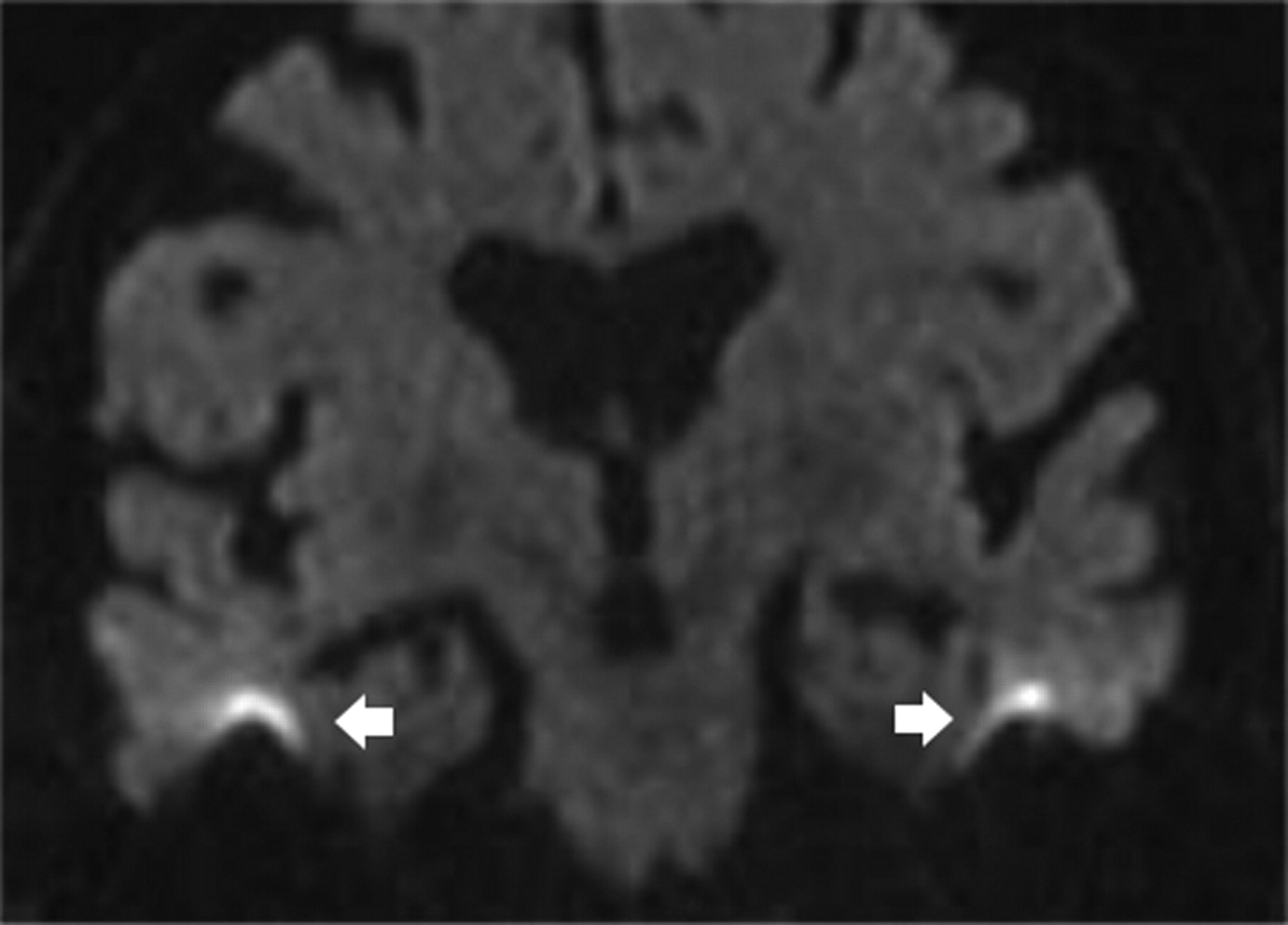
Cureus Diagnostic Accuracy Of Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Intra Cerebral Abscess By Taking Histopathological Findings As The Gold Standard

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Intensity Corrected Dual Echo Echo Planar Imaging De Epi For Improved Pediatric Brain Diffusion Imaging

Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Of Primary And Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma An Assessment By Readers With Different Expertise

Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Echo Planar And Non Echo Planar Propeller Techniques In The Clinical Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro

Non Epi Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Siemens Healthineers Belgium

Epos Trade

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

Detection Of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma By Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Multishot Echo Planar Imaging Compared With Single Shot Echo Planar Imaging American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging Versus Spin Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Acquired Middle Ear Cholesteatoma American Journal Of Neuroradiology

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of 1 5 T Versus 3 T Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma In The Middle Ear And Mastoid Sciencedirect
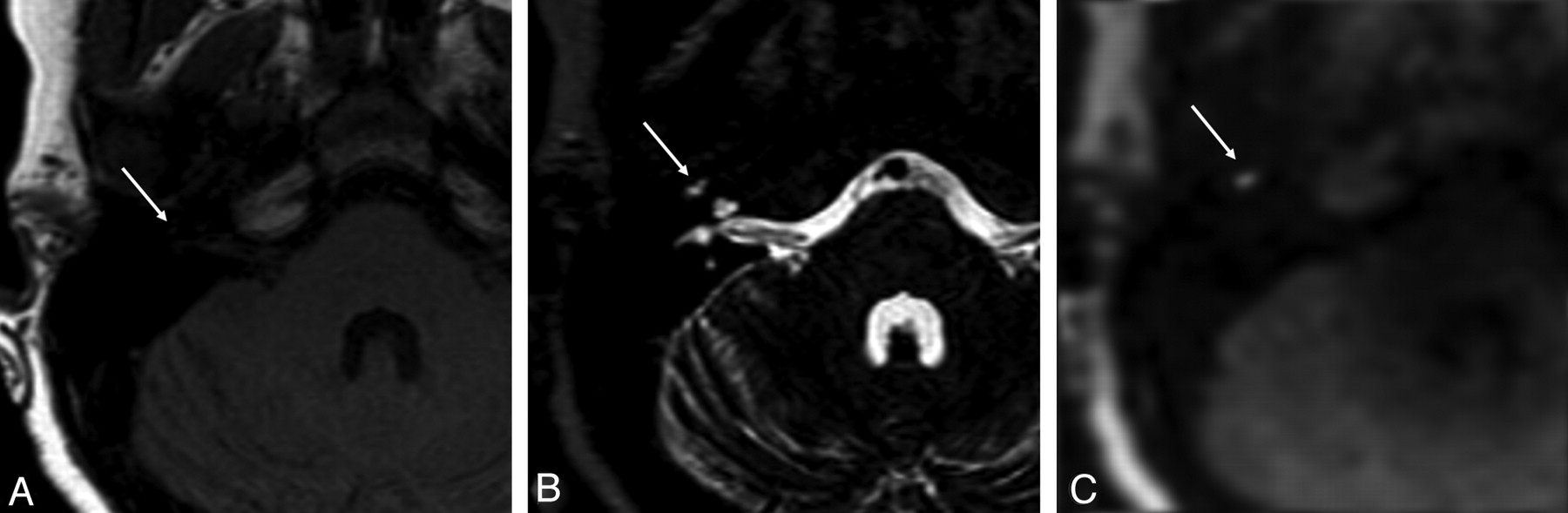
The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Comparison Of Different Dwi Techniques A Epi Dwi Acquired In A Download Scientific Diagram
Cholesteatomas

Turbo Spin Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri For Cholesteatoma In Revision Mastoidectomy A Prospective Study Of Diagnostic Accuracy And Clinical Impact Paddle Australian Journal Of Otolaryngology
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmvqltbywc Aif05fxypqcjs41z1s7i9movfx4bd4ypnfhho0f Usqp Cau
Jcm Free Full Text Texture Analysis Of Multi Shot Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma The Diagnostic Value For Nodal Metastasis Html

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics
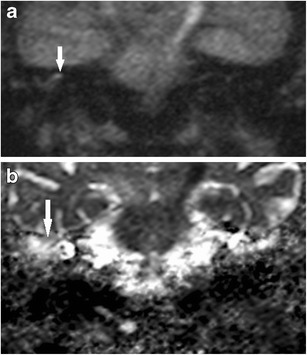
False Positive High Dwi Signal For Cholesteatoma Non C Open I
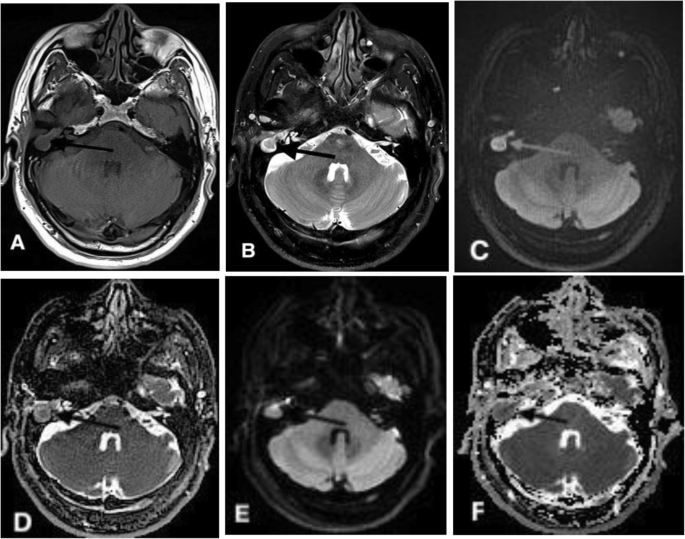
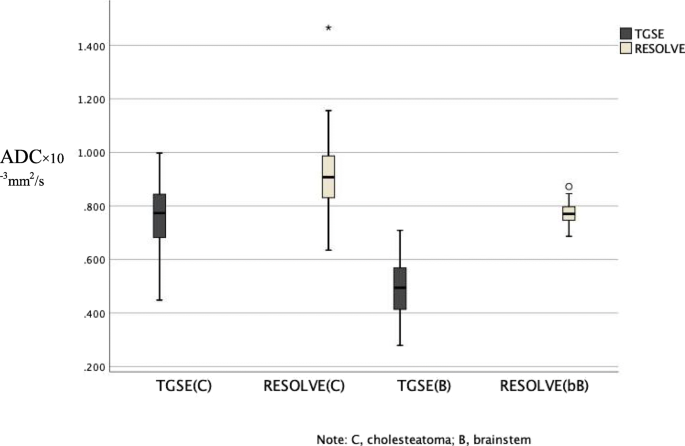
Performance Of Tgse Blade Dwi Compared With Resolve Dwi In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Bmc Medical Imaging Full Text
Magnetism Questions And Answers In Mri

Epos Trade
Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Post Operative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Navigating Beyond The Pitfalls To Find The Pearl Springerlink

Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Of Primary And Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma An Assessment By Readers With Different Expertise

Pdf Detection Of Postoperative Residual Cholesteatoma With Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Filip Deckers Academia Edu
Http Pdf Posterng Netkey At Download Index Php Module Get Pdf By Id Poster Id
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro

Epos C 0135

Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Echo Planar And Non Echo Planar Propeller Techniques In The Clinical Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma
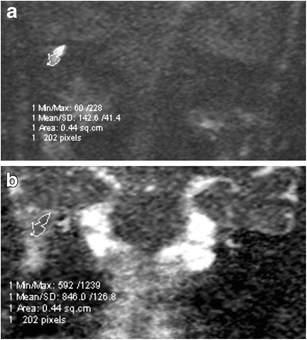
Importance Of Signal Intensity On T1 Weighted Spin Echo Sequence For The Diagnosis Of Chronic Cholesteatomatous Otitis Springerlink

Pdf Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Of Primary And Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma An Assessment By Readers With Different Expertise
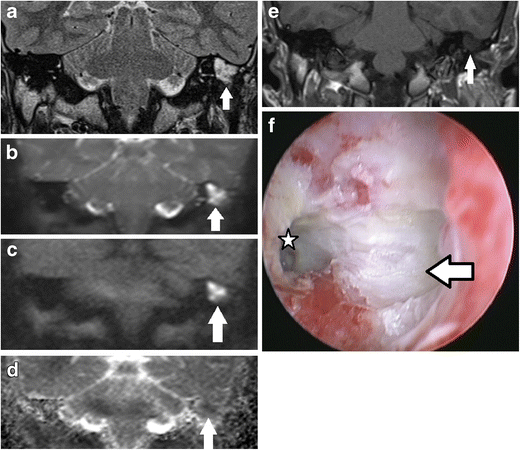
Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Post Operative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Navigating Beyond The Pitfalls To Find The Pearl Springerlink
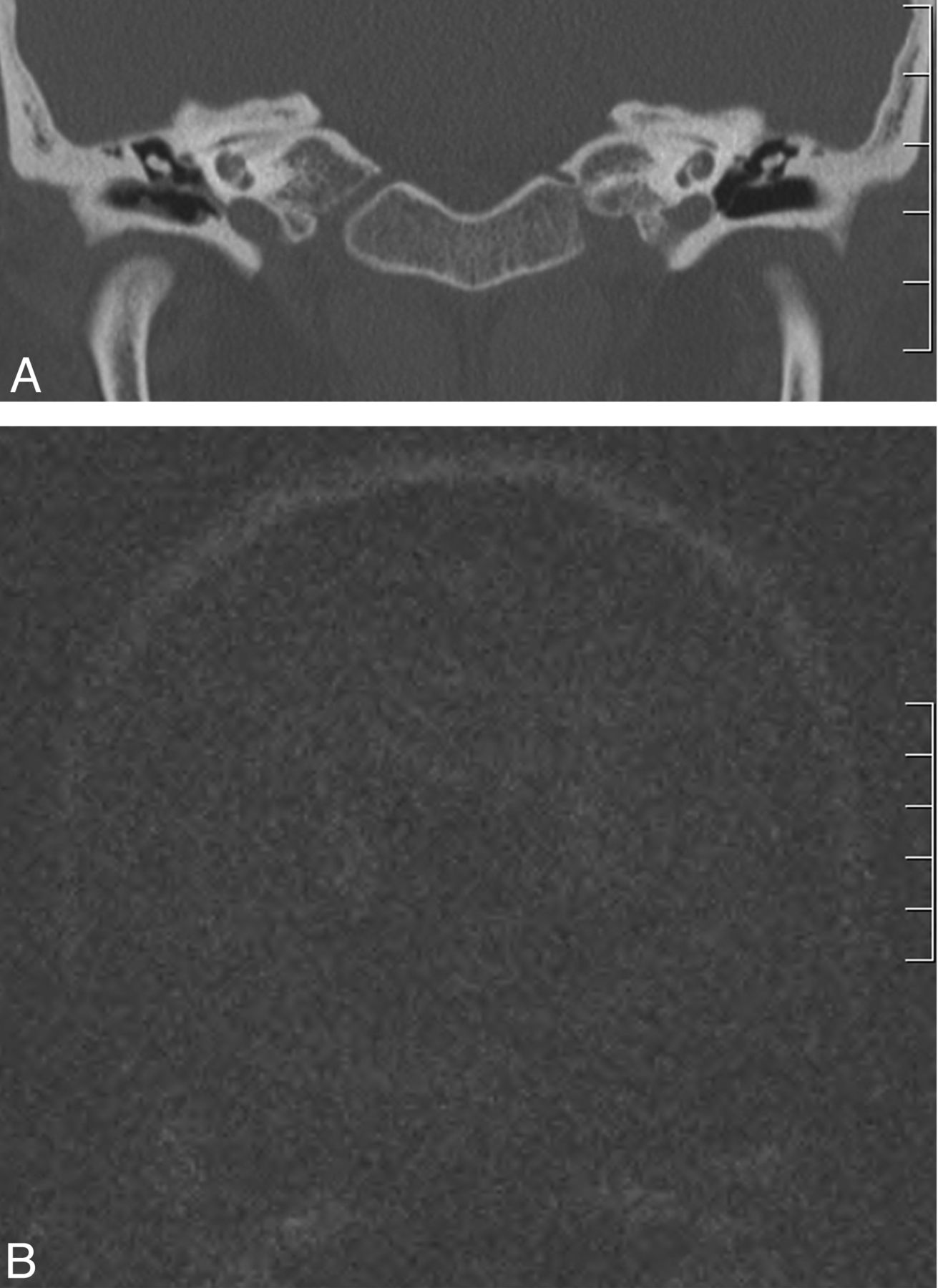
Use Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging For The Detection Of Cholesteatomas In High Risk Tympanic Retraction Pockets American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Performance Of Tgse Blade Dwi Compared With Resolve Dwi In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Bmc Medical Imaging Full Text

Non Ep Dwi Mri Cannot Replace 2nd Look Otology Neurotology Facebook
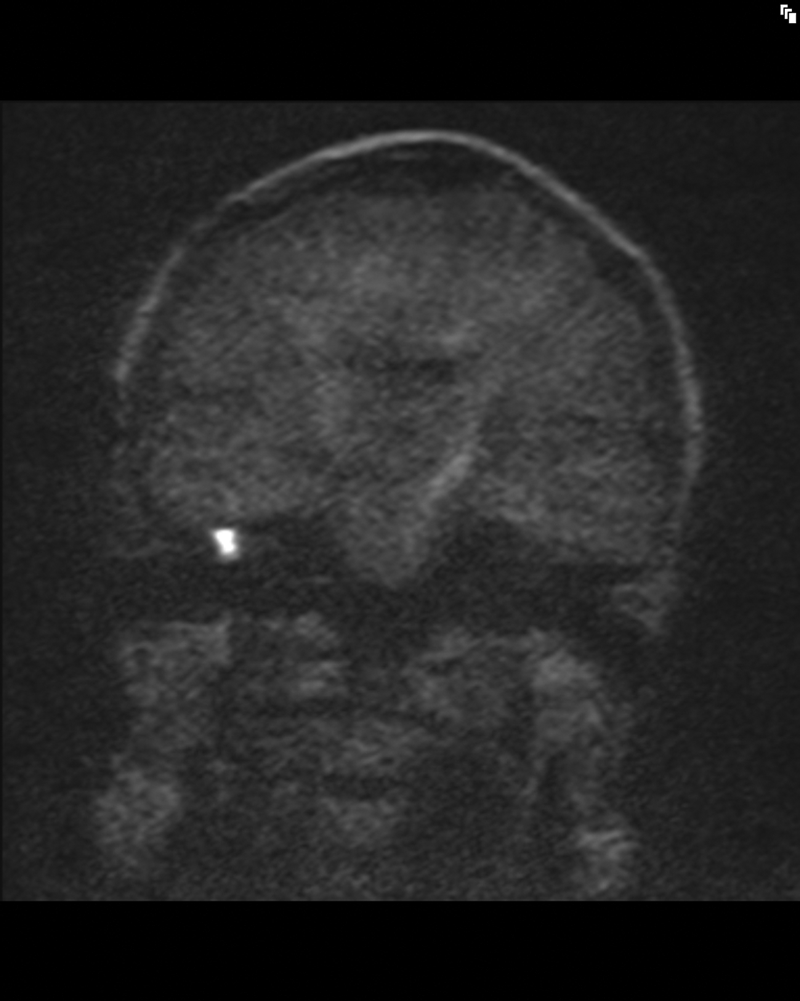
Detecting Postoperative Cholesteatoma With Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ent Audiology News

Recurrent Cholesteatoma A Echo Planar Dwi Shows Artifacts Double Download Scientific Diagram

Axial 2d Diffusion Weighted Spin Echo Echo Planar Imaging Download Table

Top Pdf About Planar Imaging 1library
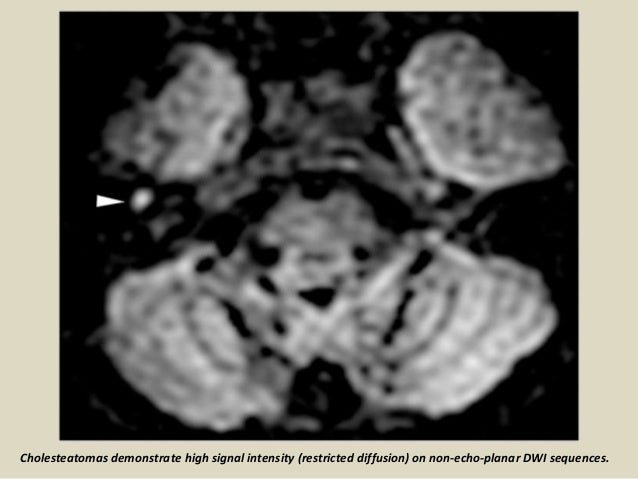
Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Imaging Of Choleteatoma
Plos One Differentiation Of Malignant And Benign Breast Lesions Added Value Of The Qualitative Analysis Of Breast Lesions On Diffusion Weighted Imaging Dwi Using Readout Segmented Echo Planar Imaging At 3 0 T

Epos Trade

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

Non Epi Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Siemens Healthineers Belgium

Dwi Of Cholesteatoma Ajnr News Digest
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics
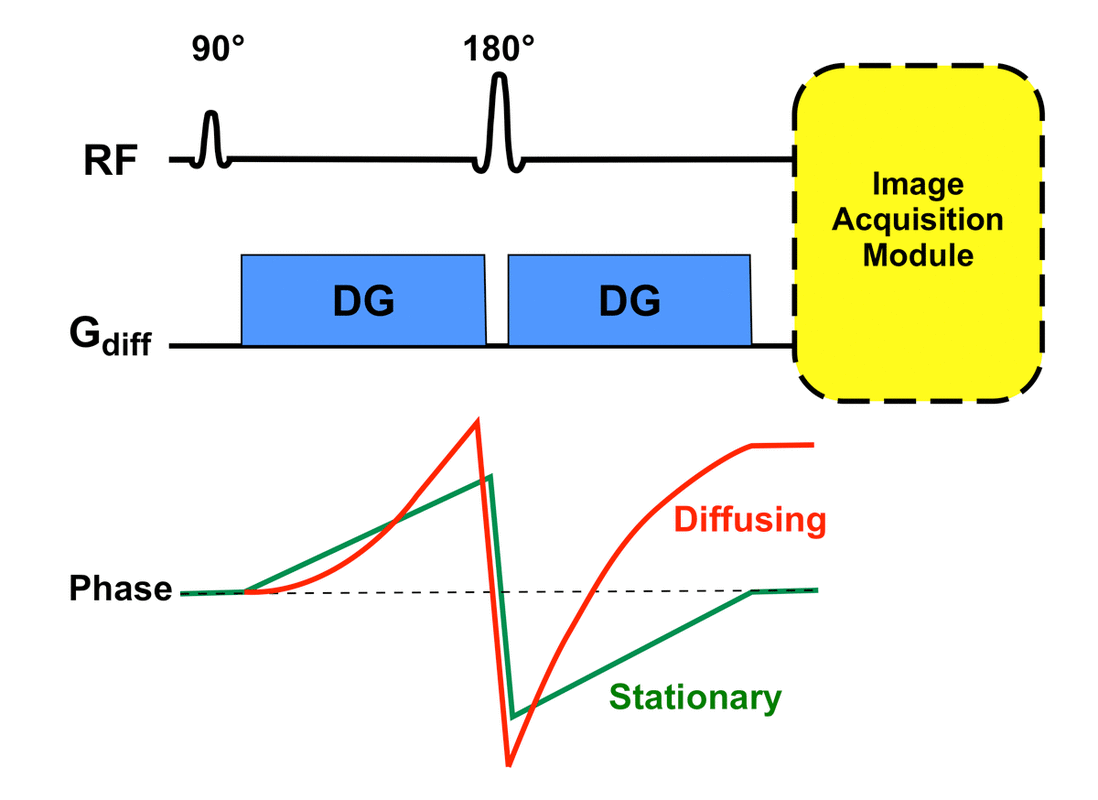
Dwi Questions And Answers In Mri

Optimization Of Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging With Parallel Imaging In Healthy Pancreas Yu Nishina1 Satoru Morita1 Tatsuya Kuramoto2 Makoto Suzuki2 Hitoshi Tadenuma2 Yasuhiro Goto2 Masami Yoneyama3 And Shuji

Turbo Spin Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri For Cholesteatoma In Revision Mastoidectomy A Prospective Study Of Diagnostic Accuracy And Clinical Impact Paddle Australian Journal Of Otolaryngology
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro

Comparison Of 2d Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo And Spin Echo Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Brain Mri At 3 0 Tesla Preliminary Experience In Children Sciencedirect
Axial And Coronal Non Epi Dwi T2 Haste At The 2 Year Follow Up Download Scientific Diagram

Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Compared Diagnostic Performances Of Two Incremental Mri Protocols Including Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Acquired On 3t And 1 5t Scanners Sciencedirect
Gale Academic Onefile Document Using Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Detecting Cholesteatoma Following Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy Our Experience With Patient Episodes

Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Echo Planar And Non Echo Planar Propeller Techniques In The Clinical Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding
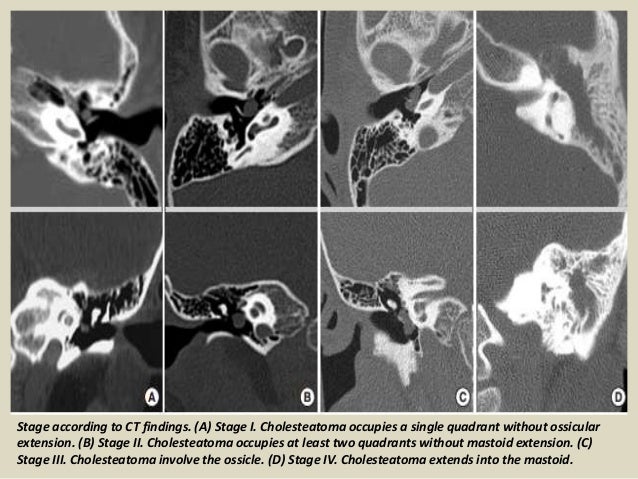
Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Imaging Of Choleteatoma



