Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted
Http Pdf Posterng Netkey At Download Index Php Module Get Pdf By Id Poster Id

Pdf Potential Value Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of The Nasopharynx A Primary Study For Differential Diagnosis Between Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma And Post Chemoradiation Fibrosis

Pdf Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Versus Delayed Gadolinium Enhanced T1 Weighted Mr Imaging Value In Detection Semantic Scholar
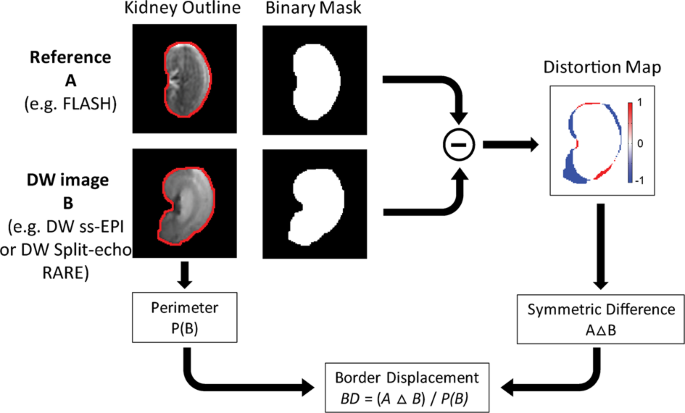
Diffusion Weighted Renal Mri At 9 4 Tesla Using Rare To Improve Anatomical Integrity Scientific Reports
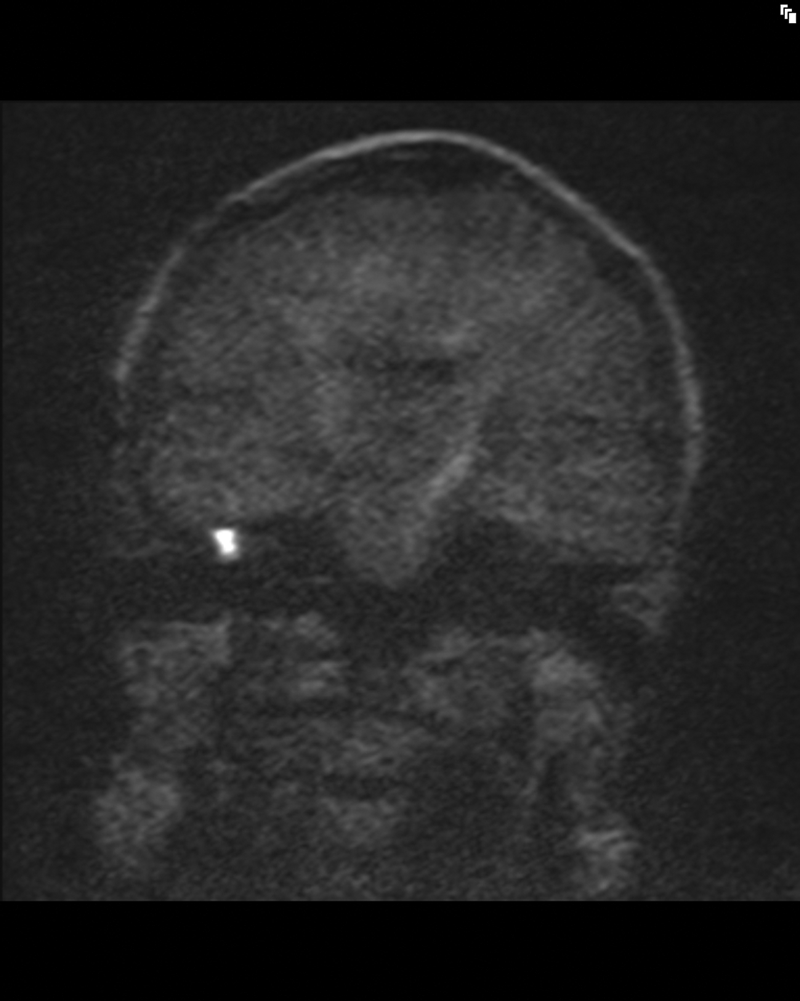
Detecting Postoperative Cholesteatoma With Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ent Audiology News

Quick Breakdown Of Echo Planar Imaging Youtube
Dremmen MH, Hofman PA, Hof JR, Stokroos RJ, Postma AA (12) The diagnostic accuracy of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the detection of residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma of the temporal bone.
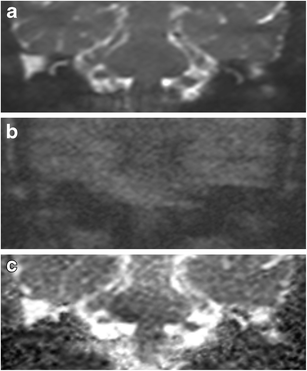
Non echo planar diffusion weighted. However, the addition of this facility involves expensive magnetic resonance scanner upgrading. The aim of this study is to define a range of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values within which. Yamashita K, Hiwatashi A, Togao O, et al.
To qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate image quality and compare the diagnostic value of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) based on turbo spin-echo (TSE) and. Non-EPI requires also shorter acquisition time in comparison to delayed postcontrast sequences conventionally used in cholesteatoma imaging 2, 4, 7, 8, 13. Wenhui Huang 1 * Wenhui Huang.
Recent studies have shown that non-echo planar (non-EPI) diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can accurately predict the presence and extent of cholesteatoma in both primary and. In the modern lexicon these are termed single shot. Compared diagnostic performances of two incremental MRI protocols including non-echo planar diffusion-weighted imaging acquired on 3T and 1.5T scanners.
The aim of this study was to determine the certainty of non-echo-planar imaging diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (non-EPI DW MRI) in the diagnosis of primary and recurrent cholesteatoma in patients with clinical suspicion of cholesteatoma, assessing the sensitivity and specificity of the test in both groups. Non-echo-planar imaging was found to be more reliable compared with echo-planar imaging in identifying residual/recurrent cholesteatoma in one systematic review. Jindal M , Riskalla A , Jiang D , Connor S , O'Connor AF ( 11 ) A systematic review of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance.
To describe the accuracy of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW MRI) in identifying middle ear cholesteatoma. To investigate the diagnostic value of non–echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) for primary and recurrent/residual (postoperative) cholesteatoma in adults (≥18 years) after canal wall up surgery. Non‐echo‐planar imaging (EPI) MRI has been recently introduced to improve the detection of small‐sized cholesteatoma and decrease different artefacts occurring in the EPI‐diffusion‐weighted (DW) technique.
Whereas this fast sequence may be sufficient to screen for residual cholesteatoma in canal. Diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) is a powerful tool for the detection of cholesteatoma. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) is an alternative to second-look surgery for the detection of cholesteatoma.
As originally defined, echo planar imaging referred to a sequence in which data from all of k-space for an entire 2D plane was collected following a single RF-excitation pulse. To examine the novel use of non-echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) in depicting activity and treatment response in active Grave's orbitopathy (GO) by assessing, with inter-observer agreement, for a correlation between its apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) and conventional Short tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) MRI signal-intensity ratios (SIRs). Research Article Head and Neck The Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Echo-Planar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Detection of Residual and/or Recurrent Cholesteatoma of the Temporal Bone M.H.G.
JAMA Otolaryngology-- Head & Neck Surgery , 142 (10), 947–53. The signal intensity should be higher than visible on the DWI images with b-value 0 s/mm 2. Non–echo-planar (EP) diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging had significantly higher sensitivity than delayed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR imaging.
Non-echo-planar DWI MR imaging (including the HASTE sequence) has been shown to be highly sensitive and specific for large cholesteatomas. More recently the term has been expanded to include any rapid gradient-echo or spin-echo sequence in which k-space is traversed in one or a small number of excitations. A meta-analysis of the published literature.
1247 - 1250 6. Role of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted images in the identification of recurrent cholesteatoma of the temporal bone Radiol Med. The diagnostic accuracy of 1.
Non-echo planar DWI is currently the imaging modality of choice due to its high diagnostic performance in the detection of post-operative cholesteatoma 1-3. S Velthuis, K J van Everdingen, J J Quak and D R Colnot, The value of non echo planar, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of residual or recurrent middle-ear cholesteatoma, The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 10.1017/S, 128, 07, (599-603), (14). The images were analysed and reported by a single, blinded consultant head and neck radiologist with experience and expertise in temporal bone imaging.
T versus 5| 3, T Non-Echo-Planar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the detection of residual or recurrent cholesteatoma in the middle ear, mastoid. Another systematic review found that non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted MRI is highly sensitive and specific in identifying middle-ear cholesteatoma. Turbo spin non echo-planar diffusion weighted imaging (NEDWI) sequences were acquired in the coronal and axial plane using a 2 cm field of view and 2 values of the diffusion gradient:.
False Positive and Negative Imaging for Cholesteatomas on Non-Echo-Planar Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Prior Tympanomastoidectomy Surgery. The combination of delayed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR imaging and non-EP DW imaging yielded no higher sensitivity than non-EP DW imaging alone. ( 13 ) Evaluating the utility of non echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the preoperative evaluation of cholesteatoma:.
This technique is also time saving in comparison to delayed post‐contrast imaging. However, the DW MRI appearances of postoperative or inflammatory mucosal changes have not been well investigated, thus rendering the interpretation of postoperative DW MRI difficult in the presence of mucosal reactions. It is the only entity that demonstrates high signal intensity on DWI.
A prospective study of 33 ears, 21 with previous cholesteatoma surgery. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Another systematic review found that non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted MRI is highly sensitive and specific in identifying middle-ear cholesteatoma.
The aim of our study was to evaluate the importance of a non-injected T1-weighted spin-echo sequence (T1WSE) combined with a non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted (non-EPDW) sequence for the pre-operative detection of cholesteatoma by the radiologist on MRI, compared to surgery. The standard examination is a T2-weighted series in the coronal and axial plane, followed by a non-echo planar DWI series (b-values 0, 1000). This diagnostic accuracy and ability to differentiate between post-surgical granulation and recidivism has led to its.
Previous studies demonstrated that, among DWI acquisition techniques, non-echo-planar imaging (EPI) MRI is a more accurate method in detecting middle ear cholesteatoma compared to EPI and it improves the detection of small-sized cholesteatoma and decreases artifacts occurring in the EPI diffusion weighted technique 1, 2, 4, 8, 11, 12;. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. However, the sequence is prone to artefact and care must be taken how the sequence is performed and interpreted 2.
To examine the novel use of non-echo-planar diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) in depicting activity and treatment response in active Grave’s orbitopathy (GO) by assessing, with inter-observer agreement, for a correlation between its apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) and conventional Short tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) MRI signal-intensity ratios (SIRs). Diffusion-weighted imaging is particularly useful when distinguishing a cholesteatoma from other middle ear masses. This was a prospective study of 16 patients who.
Compared with the EP DWI sequence, the non-echo-planar diffusion weighted imaging (non-EPI) DW imaging sequence produces thinner slices and has a higher imaging matrix, and it tends to produce fewer magnetic susceptibility artifacts but requires longer imaging times (multi-shot non-echo-planar DWI sequences require approximately 8 min), and non. With CWU surgery, residual disease can be monitored through the use of non-echo planar diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) if second-look surgery is to be avoided. To describe the accuracy of non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW MRI) in identifying middle ear cholesteatoma.A meta-analysis of the published literature.A systematic review of the literature was performed to identify studies in which patients suspected of having middle ear cholesteatoma underwent DW MRI scans prior to surgery.
Non echo planar, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction sequence) compared with echo planar imaging for the detection of middle-ear cholesteatoma. Li PM , Linos E , Gurgel RK et al. In this retrospective case review, 113 patients with chronic otitis underwent surgery (gold standard) for a clinical.
Non-echo-planar imaging was found to be more reliable compared with echo-planar imaging in identifying residual/recurrent cholesteatoma in one systematic review. Non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging represents an alternative to resolve this problem, once this method is less subject to this type of artifact, besides offering images with higher spatial resolution and thinner slice thickness, allowing the detection. Diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is emerging as an alternative to second-look surgery in ruling out residual or recurrent disease after cholesteatoma eradication.
View This Abstract Online;. To assess the utility of DWI with echo-planar (EPI-DWI) and non-echo-planar (PROPELLER) sequences for the diagnosis of primary and recurrent cholesteatoma. A primary study for differential diagnosis between recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma and post-chemoradiation fibrosis Show all authors.
Jindal M, Riskalla A, Jiang D, et al. A systematic review of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of postoperative cholesteatoma. High-resolution three-dimensional diffusion-weighted MRI/CT image data fusion for cholesteatoma.
Even in diagnostic testing with high sensitivity and specificity, false positives and false negatives occur. Non-echo-planar imaging was found to be more reliable compared with echo-planar imaging in identifying residual/recurrent cholesteatoma in one systematic review. Non-echo planar DWI is superior for the.
The non-echo planar diffusion-weighted MRI (non-EP DWI) sequence is efficient in identifying the restricted diffusion in the substance of cholesteatoma, and, thanks to its sensitivity and precision, has changed the way otolaryngologists manage chronic ear disease. Non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging is superior to routine echo-planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as it minimises susceptibility artefacts;. To evaluate non echo-planar diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (non-EP DW MRI) at 9 months after primary surgery to rule out residual cholesteatoma in patients scheduled before second-look-surgical exploration.
Developed by renowned radiologists in each specialty, STATdx provides comprehensive decision support you can rely on - Pars Flaccida Cholesteatoma. The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of HASTE DWI for the detection of incipient cholesteatoma in high-risk retraction pockets. Recently, non-echo planar diffusion-weighted MR imaging (non-EP DW MRI) has gained much atten-tion due to its short acquisition time and high sensitivity and specificity for detecting even small cholesteatomas of 2 - 3 mm in size 1.
Errors Made in HASTE:. This study retrospectively compares diagnostic performance of 1.5 T versus 3 T non-echo planar diffusion weighted imaging with or without additional T1 and T2 sequences in the detection of residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and in particular diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) have been broadly proven to be the reference imaging method to discriminate between cholesteatoma and noncholesteatomatous middle ear lesions, especially when high tissue specificity is required.
Non-echo planar diffusion weighted MRI (NEDWI MRI) is accurate in detecting cholesteatoma in the post-operative ear but the effect on surgical decision-making in the setting of revision mastoid surgery using surgical histopathology as the gold standard has not been investigated. A systematic review of the literature was performed to identify studies in which patients suspected of having middle ear cholesteatoma underwent DW MRI scans prior to surgery. Fusion of Computed Tomography and PROPELLER Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Detection and Localization of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma.
Epub 19 Sep. Developed by renowned radiologists in each specialty, STATdx provides comprehensive decision support you can rely on - Pars Tensa Cholesteatoma. Over the past decade, numerous imaging studies have been performed looking into detection of cholesteatomas, investigating both echo planar imaging (EPI) and non-EPI DWI sequences.
On the DWI images with b-value 1000 s/mm 2, a cholesteatoma becomes apparent as a hyperintense area. Authors Andrea Romano 1. We prospectively assessed the diagnostic accuracy of MRI including delayed post.
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Rg
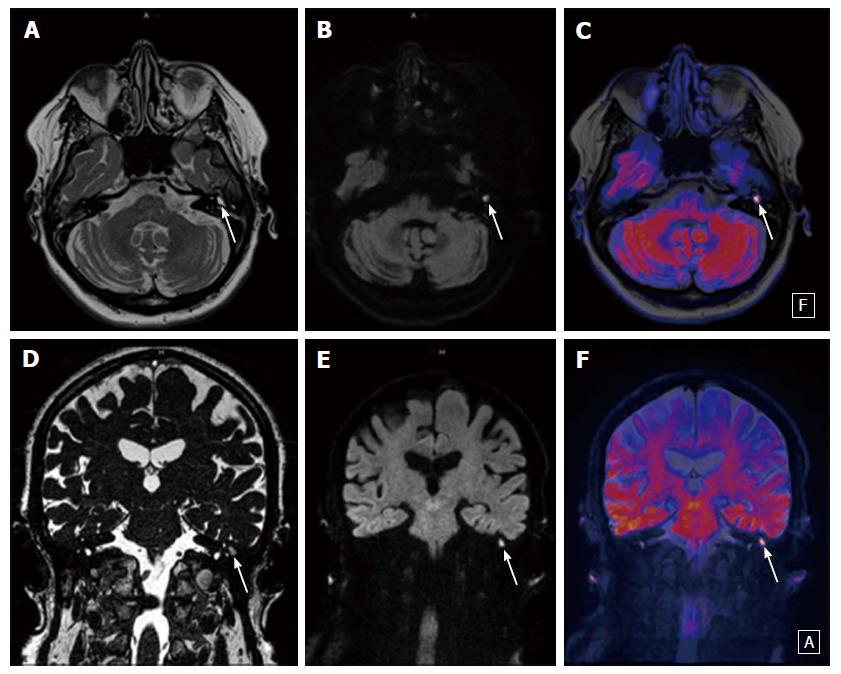
Diffusion Weighted Imaging For The Detection And Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma

Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Echo Planar And Non Echo Planar Propeller Techniques In The Clinical Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma

Detection Of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma By Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Multishot Echo Planar Imaging Compared With Single Shot Echo Planar Imaging American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Pdf Evaluation Of Acquired Cholesteatoma With Propeller Diffusion Imaging Mahmoud Abd El Ghaffar Academia Edu

Dwi Of Cholesteatoma Ajnr News Digest

Resolve Multishot Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Clinical Mri
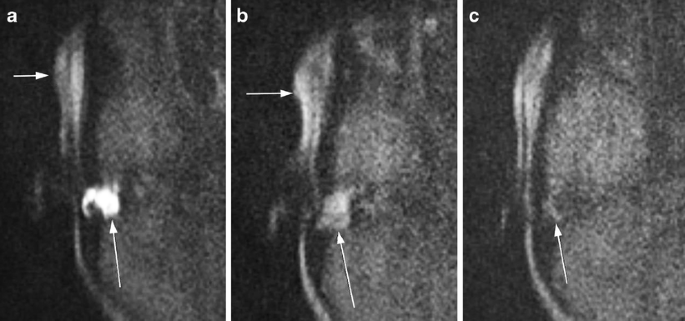
Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Children And Adolescents With Cholesteatoma Reliability And Pitfalls In Comparison To Middle Ear Surgery Springerlink

Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Of Primary And Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma An Assessment By Readers With Different Expertise
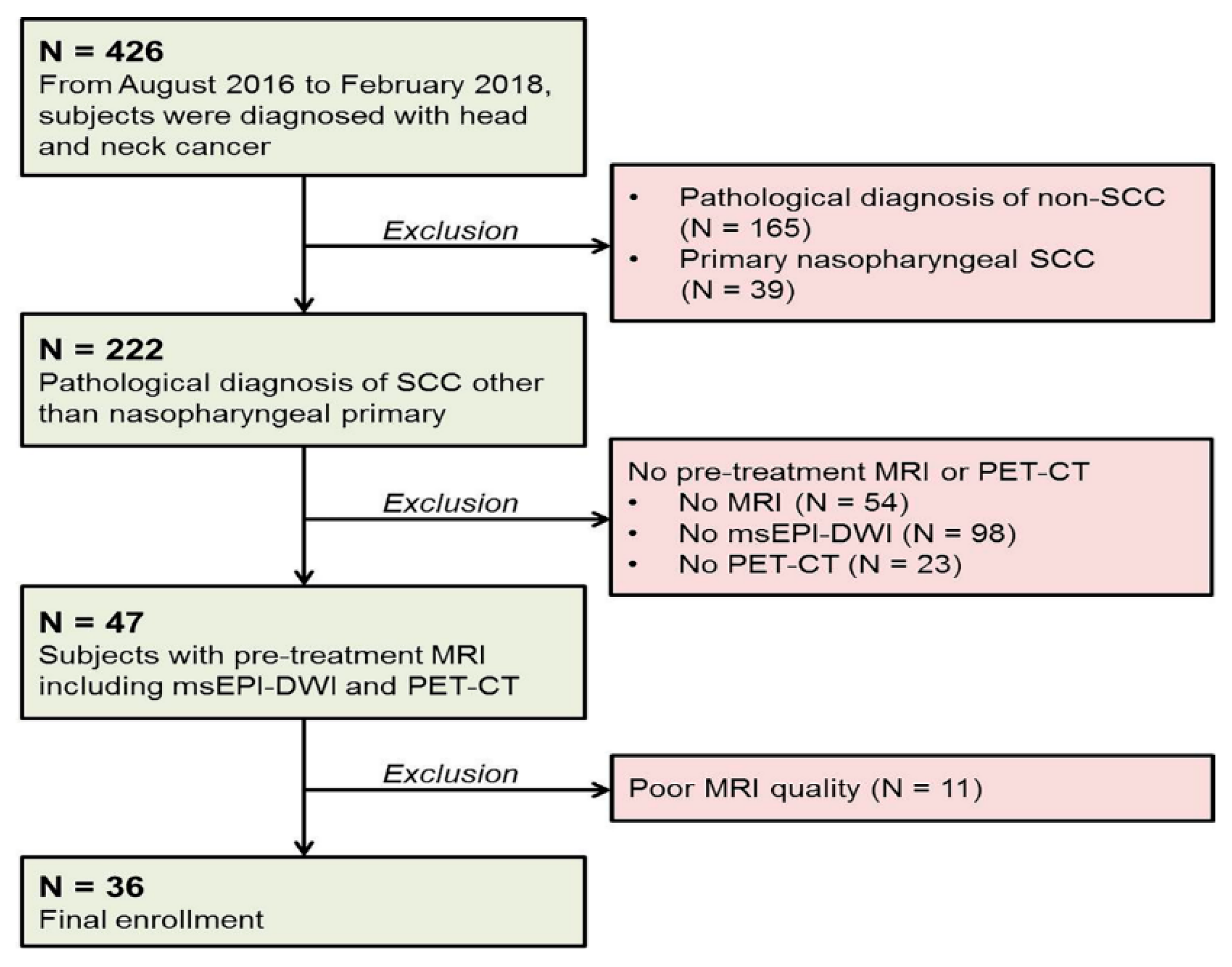
Jcm Free Full Text Texture Analysis Of Multi Shot Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma The Diagnostic Value For Nodal Metastasis Html

Non Ep Dwi Mri Cannot Replace 2nd Look Otology Neurotology Facebook

Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Post Operative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Navigating Beyond The Pitfalls To Find The Pearl Springerlink

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone American Journal Of Neuroradiology
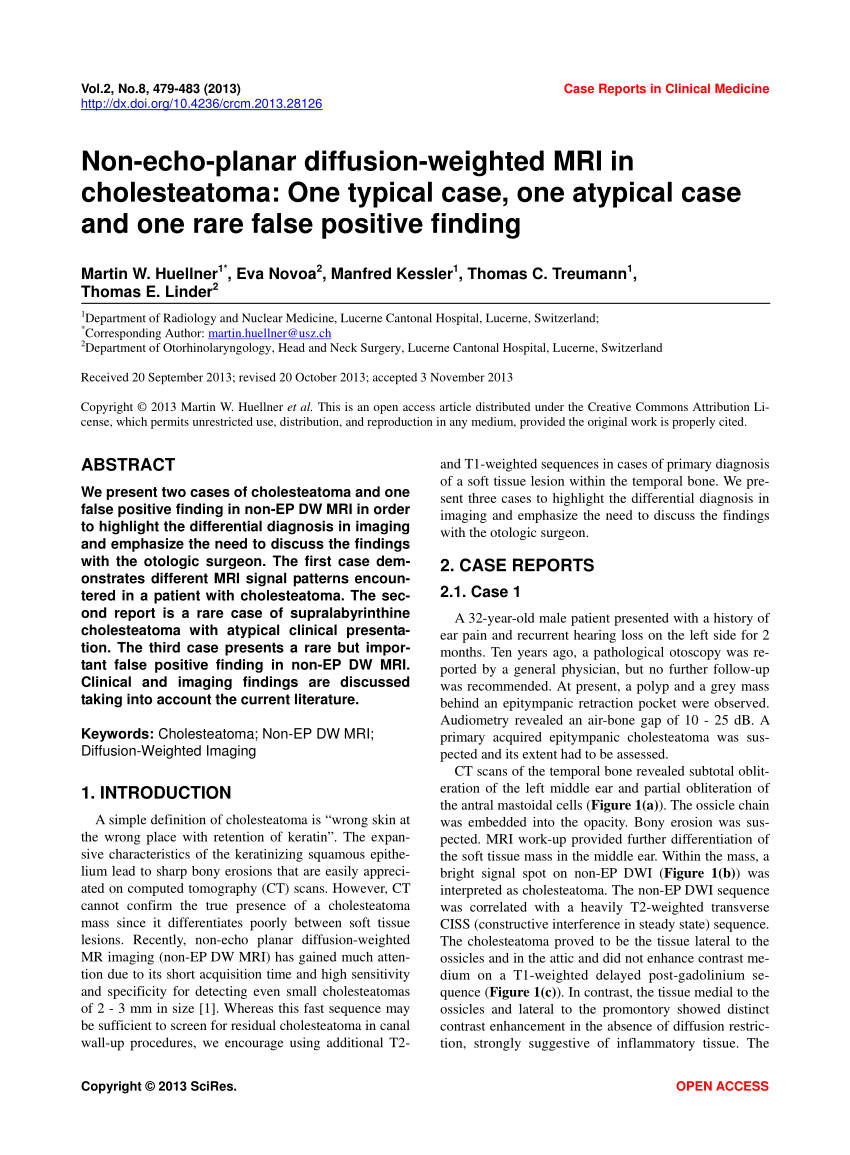
Pdf Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Radiol

Diffusion Weighted Imaging

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Periodically Rotated Overlapping Parallel Lines With Enhanced Reconstruction Sequence Compared With Echo Planar Imaging For The Detection Of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma The Journal Of
Http Pdf Posterng Netkey At Download Index Php Module Get Pdf By Id Poster Id

Gross Tumour Volume Delineation In Anal Cancer On T2 Weighted And Diffusion Weighted Mri Reproducibility Between Radiologists And Radiation Oncologists And Impact Of Reader Experience Level And Dwi Image Quality Radiotherapy And

Evaluating The Utility Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Preoperative Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma A Meta Analysis Li 13 The Laryngoscope Wiley Online Library
Plos One Differentiation Of Malignant And Benign Breast Lesions Added Value Of The Qualitative Analysis Of Breast Lesions On Diffusion Weighted Imaging Dwi Using Readout Segmented Echo Planar Imaging At 3 0 T

Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of The Brain At 7 T With Echo Planar And Turbo Spin Echo Sequences Preliminary Results Sciencedirect
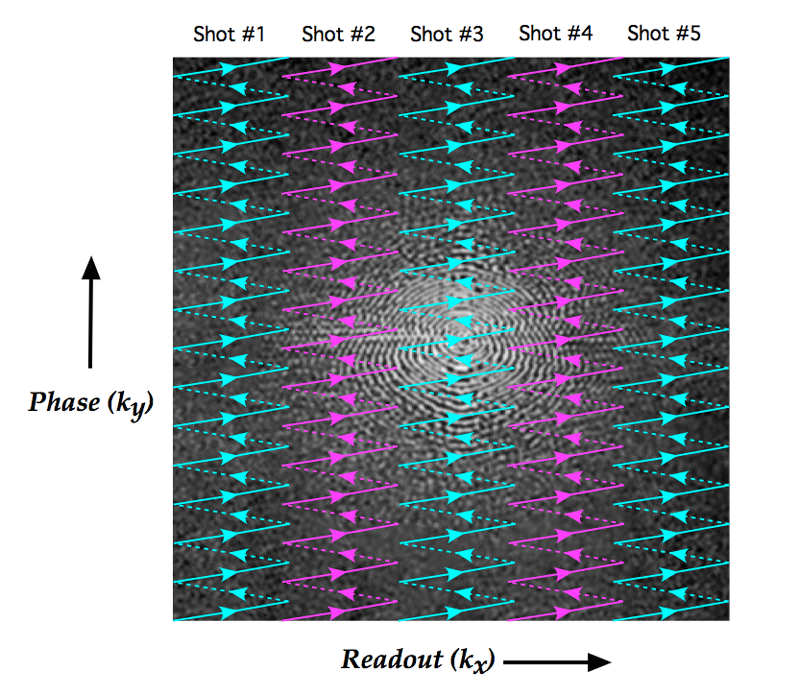
Magnetism Questions And Answers In Mri

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding

Turbo Spin Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri For Cholesteatoma In Revision Mastoidectomy A Prospective Study Of Diagnostic Accuracy And Clinical Impact Paddle Australian Journal Of Otolaryngology

Pdf Detection Of Postoperative Residual Cholesteatoma With Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Filip Deckers Academia Edu

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of 1 5 T Versus 3 T Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma In The Middle Ear And Mastoid Sciencedirect
Intensity Corrected Dual Echo Echo Planar Imaging De Epi For Improved Pediatric Brain Diffusion Imaging

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

Turbo Spin Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri For Cholesteatoma In Revision Mastoidectomy A Prospective Study Of Diagnostic Accuracy And Clinical Impact Paddle Australian Journal Of Otolaryngology

Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging Of Primary And Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma An Assessment By Readers With Different Expertise

Phantoms For Diffusion Weighted Imaging And Diffusion Tensor Imaging Quality Control A Review And New Perspectives
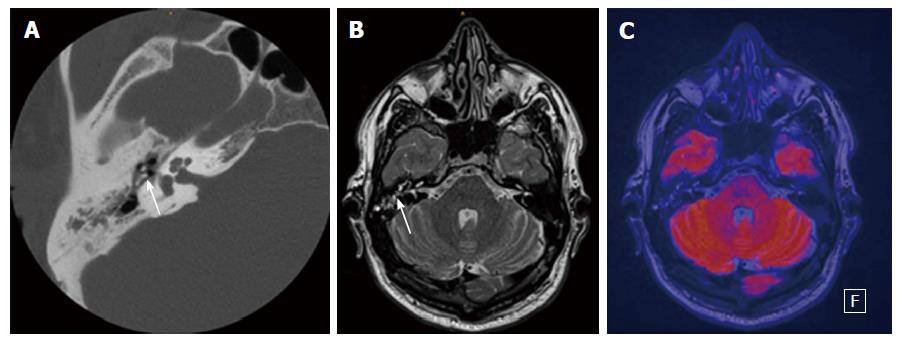
Diffusion Weighted Imaging For The Detection And Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding
2

Presentation1 Radiological Application Of Diffusion Weighted Mri In

Epos C 1923

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone American Journal Of Neuroradiology
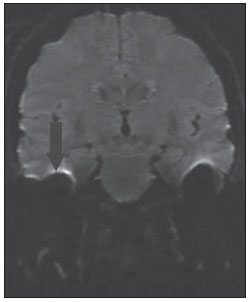
Radiologia Brasileira Colesteatoma Utilidade Da Sequencia De Difusao Sem Em Echoplanar Em Sup Sup
Presentation1 Radiological Application Of Diffusion Weighted Images

Turbo Spin Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri For Cholesteatoma In Revision Mastoidectomy A Prospective Study Of Diagnostic Accuracy And Clinical Impact Paddle Australian Journal Of Otolaryngology
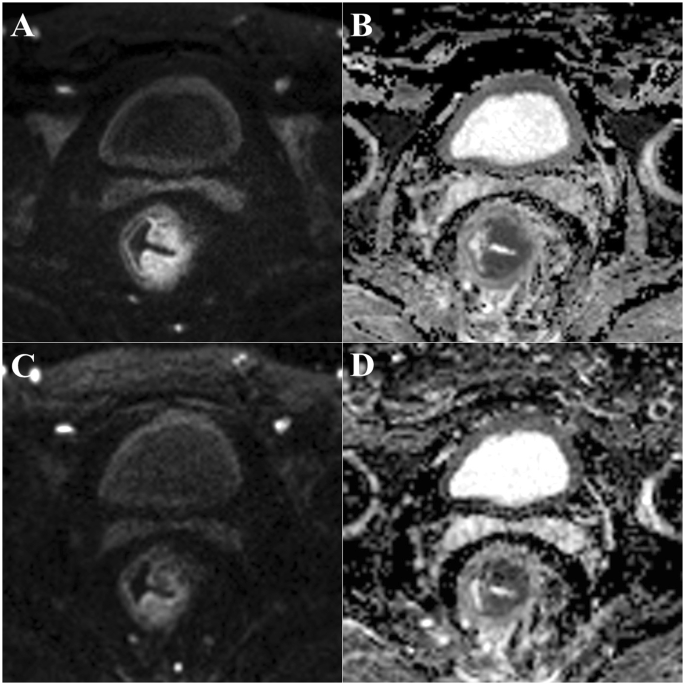
Readout Segmented Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mr For The Evaluation Of Aggressive Characteristics Of Rectal Cancer Scientific Reports

Axial 2d Diffusion Weighted Spin Echo Echo Planar Imaging Download Table

Pdf A Systematic Review Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging For Detection Of Primary And Postoperative Cholesteatoma
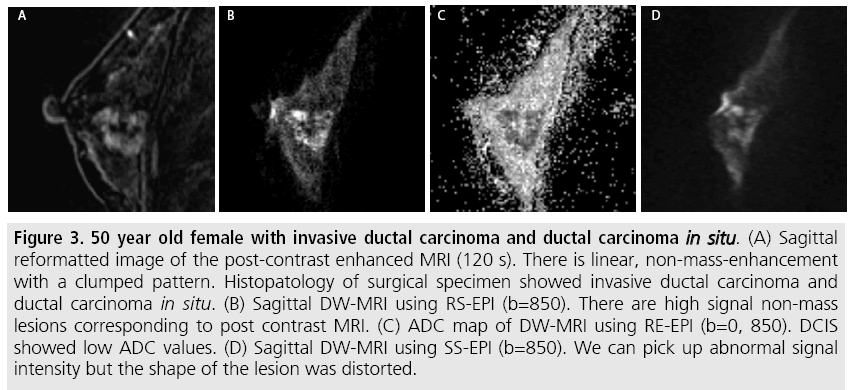
High Resolution Diffusion Weighted Mri Of The Breast Using Readout Segmented Epi And Single Shot Epi

Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Compared Diagnostic Performances Of Two Incremental Mri Protocols Including Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Acquired On 3t And 1 5t Scanners Sciencedirect

Mri Sequences Echo Planar Epi

A Pictorial Review Of Implantable Hearing Devices What Does The Surgeon Want To Know Id 91 Eshnr 18 31st Annual Meeting And Refresher Course

Imaging Evaluation Of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Iconographic Essay

Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Mri Otology Neurotology Facebook

Apparent Diffusion Coefficients For Detection Of Postoperative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma On Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Images Semantic Scholar

Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Echo Planar And Non Echo Planar Propeller Techniques In The Clinical Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma

High Resolution Diffusion Weighted Imaging Using Readout Segmented Echo Planar Imaging Parallel Imaging And A Two Dimensional Navigator Based Reacquisition Porter 09 Magnetic Resonance In Medicine Wiley Online Library
Gale Academic Onefile Document Using Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Detecting Cholesteatoma Following Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy Our Experience With Patient Episodes

Figure 4 From Cholesteatoma Utility Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Semantic Scholar

Diffusion Weighted Imaging With Dual Echo Echo Planar Imaging For Better Sensitivity To Acute Stroke

Pdf Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas An Audit

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone Ajnr News Digest

Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Echo Planar And Non Echo Planar Propeller Techniques In The Clinical Evaluation Of Cholesteatoma
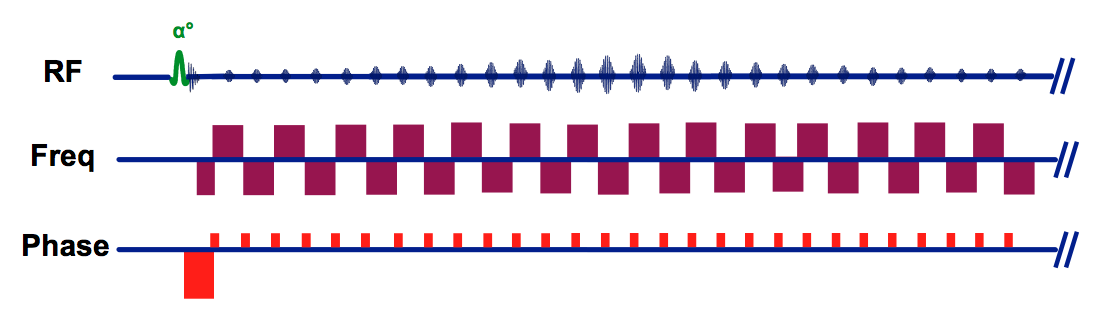
Echo Planar Imaging Epi Questions And Answers In Mri

Figure 3 From Cholesteatoma Utility Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Semantic Scholar
Intensity Corrected Dual Echo Echo Planar Imaging De Epi For Improved Pediatric Brain Diffusion Imaging

Comparison Of 2d Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo And Spin Echo Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Brain Mri At 3 0 Tesla Preliminary Experience In Children Sciencedirect

Detectability And Anatomical Correlation Of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Using Fused Thin Slice Non Echo Planar Imaging Diffusion Weighted Image And Magnetic Resonance Cisternography Fts Nepid Semantic Scholar

Resolve
Http Www Ajnr Org Content Early 14 05 08 Ajnr A3952 Full Pdf

Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Children And Adolescents With Cholesteatoma Reliability And Pitfalls In Comparison To Middle Ear Surgery Semantic Scholar

Analysis Of Phase Error Effects In Multishot Diffusion Prepared Turbo Spin Echo Imaging Van Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery

Fig 4 Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging Versus Spin Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Acquired Middle Ear Cholesteatoma American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro
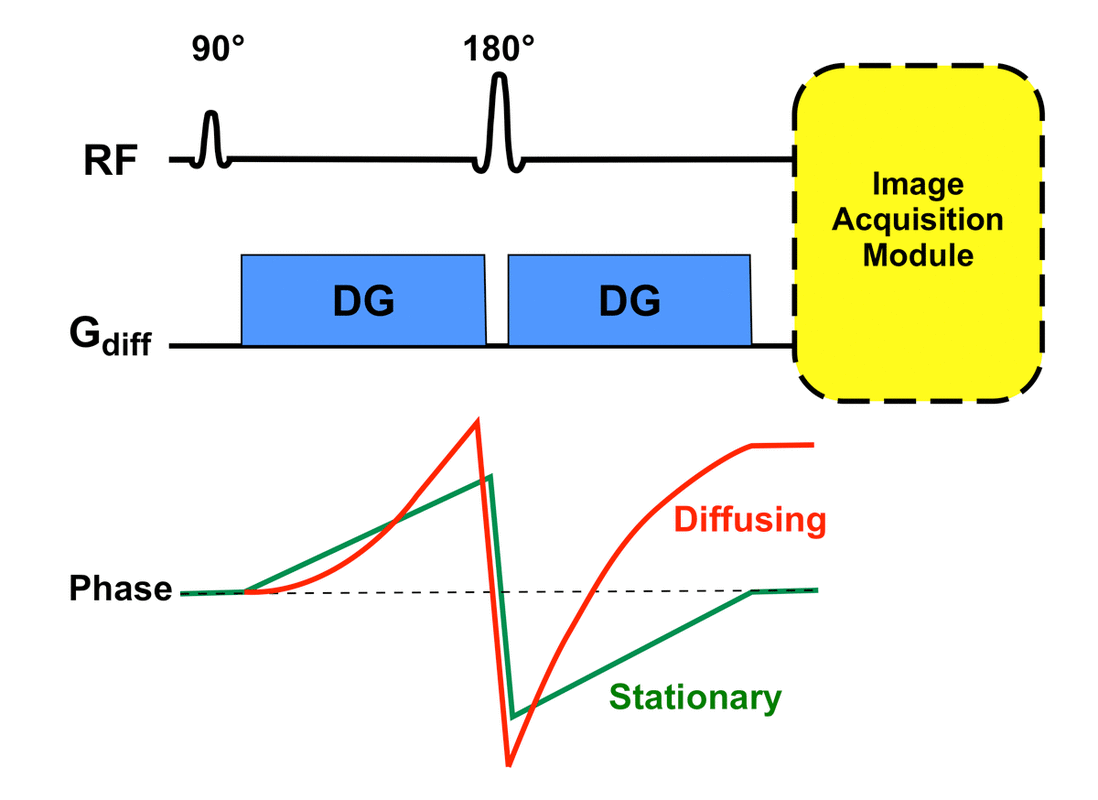
Dwi Questions And Answers In Mri

Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging Versus Spin Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Acquired Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Ajnr News Digest

Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro
Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro
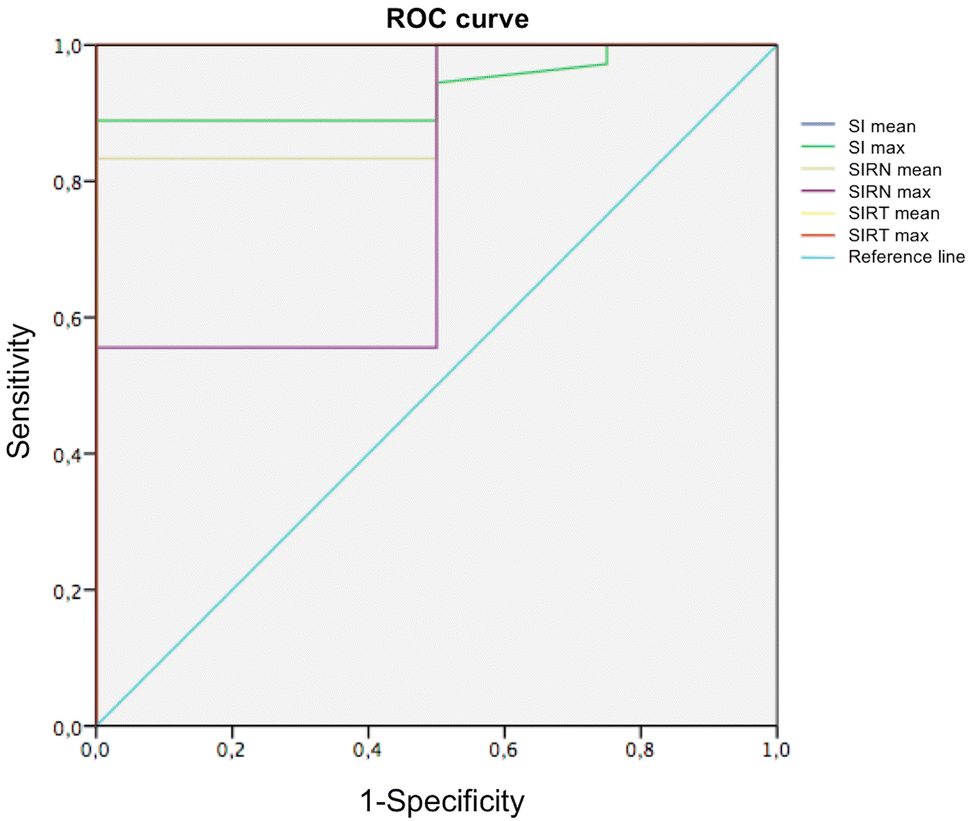
Role Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Images In The Identification Of Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone Springerlink

Pdf Non Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Post Operative Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Navigating Beyond The Pitfalls To Find The Pearl

Accuracy Of Turbo Spin Echo Diffusion Weighted Imaging Signal Intensity Measurements For The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Abstract Europe Pmc

The Utility Of Diffusion Weighted Imaging For Cholesteatoma Evaluation American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Contemporary Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging Of Middle Ear Cholesteatomas Radiographics

Epos Trade

The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Imaging In The Detection Of Residual And Or Recurrent Cholesteatoma Of The Temporal Bone American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding

Pdf The Value Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging For The Detection Of Residual Or Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma
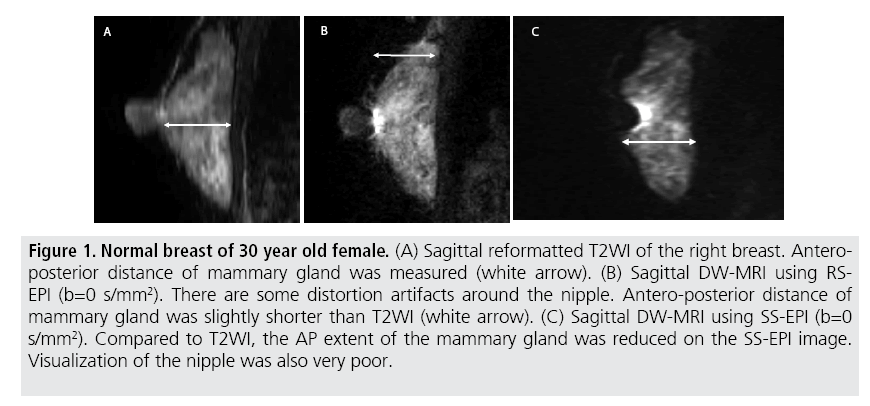
High Resolution Diffusion Weighted Mri Of The Breast Using Readout Segmented Epi And Single Shot Epi

Non Epi Diffusion Weighted Mr Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Cholesteatoma Siemens Healthineers Belgium
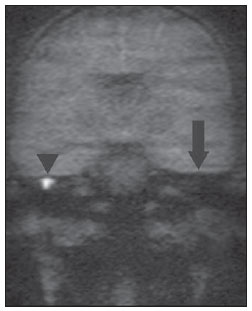
Radiologia Brasileira Colesteatoma Utilidade Da Sequencia De Difusao Sem Em Echoplanar Em Sup Sup

Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Mri In Cholesteatoma One Typical Case One Atypical Case And One Rare False Positive Finding

Epos Trade

Diffusion Weighted Imaging Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
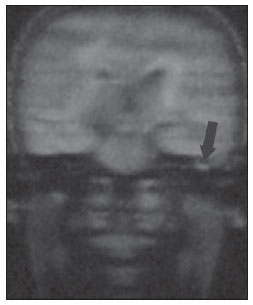
Radiologia Brasileira Colesteatoma Utilidade Da Sequencia De Difusao Sem Em Echoplanar Em Sup Sup

Pdf The Value Of Non Echo Planar Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging For The Detection Of Residual Or Recurrent Middle Ear Cholesteatoma



